

Correctly configuring the robots.txt file for affiliate website structures and marketing strategies can significantly boost search engine presence. However, getting this wrong as AI large language models become integral to search algorithms could lead to missed opportunities. Technical SEO authority Fili Wiese writes on mastering this delicate balancing act for iGBA.
In the rapidly evolving digital marketplace, technical SEO remains crucial for affiliate marketers. An often-overlooked key SEO tool is the robots.txt file. This plain text file, when optimised, can significantly improve search engine interaction with your affiliate website.
In a time when the news is dominated by artificial intelligence developments, especially large language models like GPT-4 (OpenAI), Llama2 (Meta) and Bard/Gemini (Google), proper use of robots.txt is becoming increasingly more important. Search engines continue to evolve and reshape the digital landscape.
Optimising your robots.txt file is therefore essential for your affiliate website’s content effective indexation and visibility in Google.
What is robots.txt?
The robots.txt file, nested at the root of a website, guides search engine crawlers and other bots, directing them on which parts of the website to access or to avoid. Its main function is to manage bot traffic to prevent server overload.
At the same time it also plays a crucial role in SEO by managing content visibility. Proper configuration ensures that only relevant, high-quality content is indexed, boosting a website’s search engine presence.
However, robots.txt is often misunderstood. Website owners have used robots.txt to block landing pages from being shown in the search results, not realising that by blocking search engine crawlers using robots.txt they may accomplish the exact opposite.
And that these landing pages are shown in the search results. This happens because search engines can’t crawl the page and find the meta noindex instruction, instead they see the page exists due to either internal or external linking and may still show the URL as a search result.
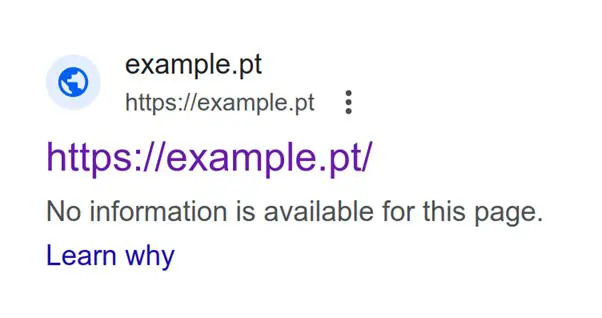
Landing pages blocked in the robots.txt file can and often are indexed, with poor snippet representation.
It is also important to note that the robots.txt file offers neither privacy nor security. It’s more of a request than a hard rule. Compliant search engines honour these requests, but it’s not a safeguard against all rogue bots or crawlers. But what is compliant?
Until 2022 there was not even an official protocol, just an official best practices document dating back to 1994. In 2019, Google published a draft for a new Robots Exclusion Protocol which was accepted in 2022.
Still even now, adhering to robots.txt directives is neither mandatory or legally binding. In the end, it is up to each bot to either be a “good” bot, respecting robots.txt or a “bad” bot ignoring robots.txt. If you want to verify if a search engine crawler is valid, you can check the IP address at SEOapi.com.
Robots.txt in technical SEO
For affiliate marketers, robots.txt is strategic. Proper use ensures search engines prioritise crawling and indexing valuable pages, like product reviews or affiliate landing pages, over less critical areas like administrative pages or affiliate redirects.
This prioritisation is crucial in SEO, as it helps efficiently utilise the crawl budget that search engines allocate to each website and prevents search engine crawlers from getting stuck in infinite loops. Moreover, incorrect use can cause significant SEO issues, like accidentally blocking important pages from search engines.
Configuring robots.txt is a delicate balancing act. It’s important to disallow sections that don’t contribute to SEO, like affiliate redirect URLs, while ensuring that affiliate product pages and articles remain crawlable.
However, over-restriction can lead to loss of potential traffic, as search engines won’t index parts of the website that might have relevant content.
Case studies show a well-configured robots.txt can boost a website’s visibility. For instance, an ecommerce website may exclude pages with duplicate content, like printer-friendly versions, while ensuring product pages are crawlable.
That said, the robots.txt directives are often a last resort when other SEO best practices fail, offering a simple way for search engine crawlers to prioritise important pages.
Sometimes you may depend on third parties, like using a CDN with bot defence measures, such as Cloudflare, inadvertently creating many useless URL patterns for search engine crawlers. The robots.txt file offers a solution. For Cloudflare, add this snippet to your robots.txt:
User-Agent: *
Disallow: /cdn-cgi/
This snippet prevents good bots like Googlebot from accessing Cloudflare bot challenge pages.
Training large language models
The advent of large language models, such as GPT-4, Bard and Llama2, has ushered in a new era for search engine algorithms. These large language models promise to understand context, intent and nuanced meanings of user queries as well as the website’s content.
Although this promise has yet to be realised, technical SEO remains crucial for indexing content. Without technical SEO, including proper use of robots.txt, your affiliate website’s content may not be considered for these large language models and your visibility may suffer long term.
As these models become integral to search algorithms, their interaction with robots.txt grows in significance. These advanced algorithms can discern subtleties in website content, amplifying the importance of robots.txt in directing their crawl patterns.
For instance, if a model deems website content highly relevant to a query, but robots.txt file restricts access to this content, it can lead to missed opportunities in search rankings.
There is an ongoing discussion about source material for training commercial large language models. Copyright is not respected or attributed, and personal information has leaked into large language models.
Although a metatag solution to respect copyright and instruct large language models on content usage for training has been advocated, Google has thus far chosen robots.txt instead.
Following Google’s announcement, OpenAI, Meta and Google have released new and/or updated existing user-agent strings, and Bing has chosen to use existing metatags instead. Although these solutions don’t fully address copyright concerns, they are a step in the right direction.
Although robots.txt offers a solution to opt-out of training large language models, it doesn’t tackle their usage or implementation.
For instance, blocking Google-Extended in robots.txt from using your affiliate website’s content for training Bard/Gemini models is effective, but Google may still employ Bard/Gemini to generate and interpret your affiliate website’s content in search results, offering users an AI-enriched experience instead of displaying your affiliate website.
Practical tips for affiliate marketers
Customising the robots.txt files to fit affiliate website structures and marketing strategies is essential for affiliate marketers. Here are some key recommendations on how to succeed:
- Ensure accessibility: Make sure your key content, especially product reviews, is accessible to search engine crawlers. Disallow sections of your affiliate website that don’t contribute to your SEO goals, like admin pages, CDN bot challenge pages and/or affiliate links. Test the URL patterns you plan to block or allow in your affiliate website’s robots.txt at com.
- Balance crawl efficiency: Efficient crawling is vital. Check your Google Search Console crawl stats reports and your server log files. Don’t waste search engine crawl budget on irrelevant URL patterns. Your robots.txt guides crawlers to content that matters most for your affiliate marketing goals. If in doubt, hire an SEO professional for a deep dive analysis on the SEO health of your affiliate website.
- Stay AI-savvy: As search engines evolve with AI technologies like large language models, understanding how these changes affect your affiliate website’s content interpretation and robots.txt directives is crucial. For example, Common Crawl data often is used for the training of large language models and opting out requires covering CCBot in the robots.txt file. Regularly review and update your robots.txt to align with these advancements.
SEO’s future might include a dynamic robots.txt use, changing directives based on criteria such as user-agent type or time-based events. This flexibility can provide nuanced control over how search engines and crawlers interact with your affiliate website.
Robots.txt is a crucial but frequently overlooked SEO tool. As AI technologies advance, they will inevitably transform affiliate SEO strategies. Staying informed about these changes and grasping their impact on robots.txt management is essential for affiliate marketers to retain their competitive advantage.

Fili Wiese
Fili is the world's leading SEO expert on the topic of Google webmaster policies, Google penalties, Google's internal processes, backlink risks and link-building techniques. Fili is the only SEO expert in the world to have published SEO articles on the official Google Search Central Blog and the official Bing Webmaster Blog. He is the go-to-guy when it comes to international and technical on-page SEO and successfully solving Google penalties.